[Applies to secondary schools only.]
Cumulative GPAs can be easily configured to meet the specific requirements of your school. You set up cumulative GPA definitions at the district level. To understand the available options, refer to the appropriate section:
Notes:
| = | For an explanation of what happens to cumulative GPAs and credits when you convert your existing database to use the Permanent Record functionality, see |
| = | Current year GPA definitions (i.e., report card GPA definitions for the active year) are created at the school level. See Working with current year GPAs [>>] |
| = | A year GPA is the grade point average for a single year, using a cumulative GPA formula. |
Because cumulative GPA calculations include both current year and historical data, make sure the overall historical data on the students' historical pages does not include any current year information - keep current year grades and historical grades separate. The cumulative GPA calculations combine the historical and current year data to produce the correct cumulative GPA and if historical GPAs include current year data, cumulative calculations will not be correct. For more information, see Selecting a Calculation Formula [>>].
For any cumulative GPA definition, you can:
| = | Calculate as a potential credits grade average or a simple grade average. |
| = | Apply course adjustment factors or not, regardless of the formula chosen. |
| = | Use grade points or numeric values scaled to 100 in the calculation. |
| = | Specify that if the student is denied credit for any reason the grade should be counted as 0 in cumulative GPA calculations. |
| = | Define how to treat missing grades. |
| = | Use course leveling to apply adjustment factors. |
| = | Use either weighted or unweighted values from historical data, regardless of the formula chosen. |
| = | Control the courses by including only courses you specifically select, excluding courses you specifically select, or including all courses. A GPA can only include courses for which grades are collected, as determined by the district in the Course Catalog. |
| = | Include the best courses in the GPA definition, such as the best five courses, rather than all of the courses assigned to the GPA definition. |
All cumulative GPA calculations follow these rules:
| = | For the current year's grades and historical grades, special grades are ignored because they have no point values or numeric equivalents. |
| = | If a student is enrolled in multiple schools, the cumulative calculation includes all courses from all schools the student is enrolled in. The cumulative GPA definition used for a particular student is taken from the student's home school. |
| = | If cumulative GPA definitions are set up differently at different schools, students who are dual enrolled may be awarded different GPAs at different schools. In this case, the cumulative GPA assigned at the student's home school prints on the student's transcript and, when Year End Processing is run, rolls over to the student's historical transcript page. |
| = | On the Course Grading page at the district level, if "Exclude from GPA" is selected, then that course is not included in the cumulative GPA calculations. The "Exclude from GPA" setting supersedes the "Use in Cum GPA" setting on the Course Grading page at the school level. |
| = | For a student's grades to be included in the cumulative GPA calculation, the student must be enrolled during the time period to which the calculation applies. A new student's grades earned prior to enrollment and entered in PowerSchool SMS are not counted in the cumulative GPA calculations because the student was not enrolled during the applicable time period. A student's historical grades, are included in GPA calculations, regardless of the student's enrollment. |
| = | If a student is missing overall historical data or one or more yearly historical GPAs, the student is added to the suspect cumulative GPA list. However, if the student is also in a grade level equal to the "Start from grade level" specified on the Add/Edit Cumulative GPA page, the student's cumulative GPA is calculated using the current year data. |
| = | For historical grades, the calculation uses data from the historical course details. For further information see Entering information about student's past courses [>>] and Entering historical year records [>>]. |
Also be aware of the attendance rules for credit calculations that apply to the current year grades portion of cumulative GPA calculations. The rules are as follows:
| = | For current year grades, if both Award Credit and Use in Cum GPA on the Course Grading page are set to Yes, then the attendance rules set up on the Attendance Rules for Credit Calculations page that affect credit awarding are taken into account. |
| = | If a student is denied credit due to excessive absences based on the settings on the Attendance Rules for Credit Calculations page, then the grade is considered 0 (zero) for the cumulative GPA calculation. For example, if a student gets 87 in a course but is denied credit due to excessive absences, that course is counted as 87 in current year averages, but as 0 for cumulative GPA calculations. For information about attendance rules for credit calculations, see Setting up an attendance rule for credit calculations [>>]. |
| = | If a user enters a credit override where, for example, the calculated credits earned is 0 and it is overridden to 0.5, then the student's actual grade is used, not 0 and not the overridden credits earned. |
| = | If a student's credits earned value is 0 due to the student's grade, then the grade is used for calculations. For example, D=0 grade points in the grading table is a passing grade with 0% credit awarded. |
Note: Attendance Rules for Credit Calculations are not automatically applied to detailed historical data. That is, if you change the number of historical course attendance absences, PowerSchool SMS does not automatically change the credits earned number, i.e., to deny credits based on attendance.
The following factors apply to all cumulative GPA calculations:
| = | If an overall cumulative GPA exists on the historical transcript pages, it is used for the historical portion of the calculation. The current year portion of the calculation uses current year grades. "Overall cumulative GPA" is the Cumulative GPA value entered in the Graduation Information panel on the Student > Historical page. |
| = | If an overall cumulative GPA does not exist, the yearly GPA value is used for each historical year that has a yearly GPA. "Yearly GPA" is the Yearly GPA value in the Course Information panel on the Student > Historical > Add/Edit Historical Year page. |
| = | If at least one yearly GPA value is missing and an overall cumulative GPA does not exist, then the calculation is based on the yearly GPAs that do exist, and the item is included in the suspect cumulative GPA list. |
If you choose to set up cumulative GPAs using both grade points and numeric values scaled to 100, you must ensure that you are comparing grades using the same scale for historical and current year data. When you are using numeric values scaled to 100, this is not an issue because the scaling is done as part of the calculation. However, with the grade points method, there is no scaling.
To accommodate no scaling for grade points, you must enter overall values in all students' historical records in the same scale that you use for the Grade Points column of the grading table used for the current year data. This ensures that the grades are comparable.
When you create cumulative GPAs, you must select a calculation formula. How this calculation formula works then depends on the calculation method you use: grade points or numeric values scaled to 100.
Formula Setup Examples
For each combination, assume that no adjustment factors are applied, the GPA definitions are set up to use Unweighted values from the student's historical page, and the overall values have been entered as in [Figure 217]:
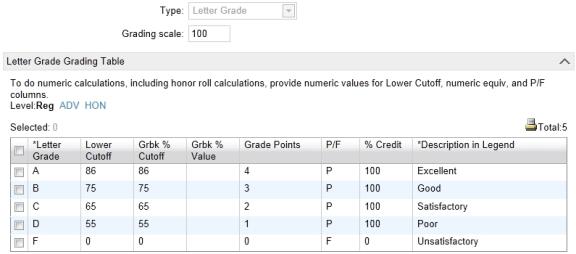
For the current year, the student took two courses, and received a B for a 6-credit course and a C for a 3-credit course. The current year grading table is set up like [Figure 218]:
Figure 217: Cumulative GPA example setup
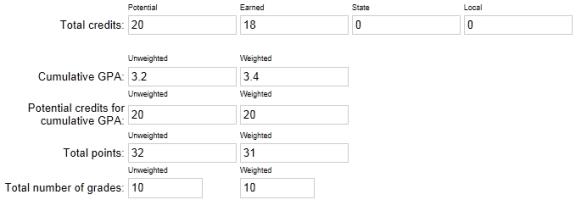
Figure 218: Cumulative GPA example
Refer to the description for each formula for details.
The "Potential Credits" for a grade item is the maximum credits for the course divided by the number of grade items within the class's schedule that have "Use in Cum GPA" set to Yes. For example, if a course has a maximum credits of 1 and it has two grade items - one in each semester - set to "Use in Cum GPA", the potential credits are calculated as 1 / 2 = 0.5. If the class only runs in one semester, the potential credits are calculated as 1 / 1 = 1.
The potential credits grade average formula weights the historical cumulative or yearly GPAs and the current year grades by multiplying them by their potential credits.
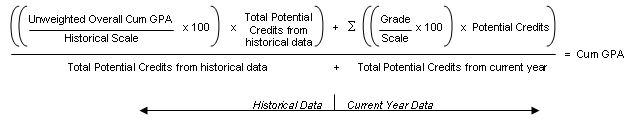
The formula for "Sum (Points x Potential Credits) / Total Potential Credits" using grade points is:
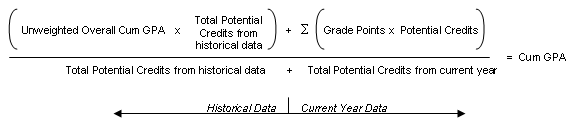
When you apply the values from the example, it looks like this:
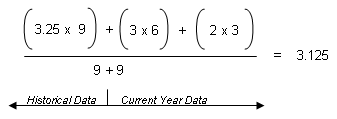
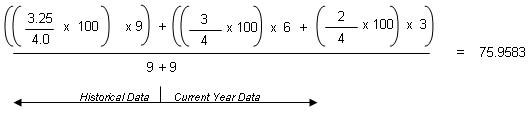
The formula for "Sum (Points x Potential Credits) / Total Potential Credits" using numeric values scaled to 100 is:
When you apply the values from the example, it looks like this:
The simple grade average formula does not use weights, so each grade is considered an equivalent unit, regardless of the potential credits.
The formula for "Sum (Points) / Total Number of Grades" using grade points is:
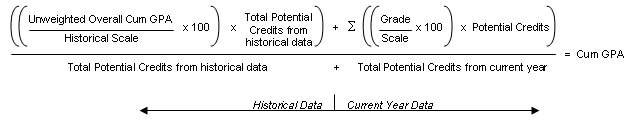
When you apply the values from the example, it looks like this:
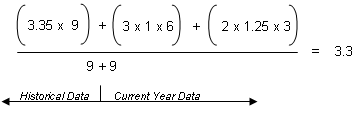
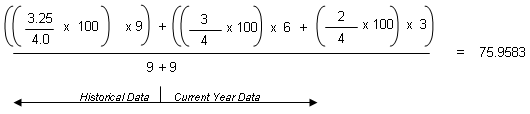
The formula for "Sum (Points) / Total Number of Grades" using numeric values scaled to 100 is:
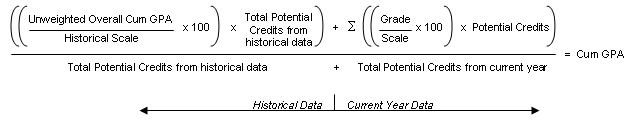
When you apply the values from the example, it looks like this:
When you edit cumulative GPAs, keep in mind that class ranks use cumulative GPAs as part of their definitions; you will need to recalculate class ranks because student ranks may be affected by your changes.
Note: If your district calculates term GPAs, PowerSchool SMS uses the formula you set up for the cumulative GPA when calculating both the end-of-term GPA and the cumulative-to-end-of-term GPA. For more information about term GPAs, see Grading periods and GPA/class rank reporting terms [>>] and Calculating term GPAs [>>].
 You can do this if your role is School Administrator.[SA]
You can do this if your role is School Administrator.[SA]
| 1 | In the Admin menu, click Grading. |
| 2 | On the Grading page, under Step 5, click Grade Point Averages. The Grade Point Averages page appears. |
| 3 | To add a cumulative GPA definition, click Add. The Add Cumulative GPA page appears. |
| = | To edit a GPA definition, select the cumulative GPA definition name and click Edit. The Edit Cumulative GPA page appears. |
| = | To delete a GPA definition, select the cumulative GPA definition to delete, click Delete. Click OK and skip the remaining steps. Note: Deleting GPA definitions will affect the class rank definitions that use them, as well as the student ranks calculated using those class rank definitions. |
| 4 | Define the cumulative GPA: |
| = | GPA Name - Enter a unique name for the GPA of up to 55 characters. If you will be using more than one cumulative GPA on a report card, ensure the name clearly differentiates the GPA from all others. |
| = | Description - If you want to describe the GPA in greater detail, enter a description of up to 200 characters. |
| = | Calculation formula - Select one of the following: |
| = | Sum (Points x Potential Credits) / Total Potential Credits |
| = | Sum (Points) / Total Number of Grades
For more details, see Working with cumulative GPAs [>>] |
| = | Adjustment factor - If you want to apply course adjustment factors to the current year portion of the calculation, select "Use course adjustment factor to determine points". Note: If your school does not apply adjustment factors in a linear way to courses (i.e., you cannot always multiply by or add the same factor to all grades), you cannot use adjustment factors in your GPAs. Instead, set up your grading tables to accommodate the different course levels (advanced, remedial, etc.). For further information, see Setting up GPA calculations (including course leveling) [>>]. |
| = | Calculation method - Select one of the following: |
| = | Use grade points - converts existing grades to the grade point equivalents specified in the grading table. |
| = | Use numeric grades scaled to 100 - divides grades entered by the appropriate scale and multiplies them by 100. |
| = | Credits earned penalty - If you want to penalize students who have not received credit, select If credits earned is zero, count grade as zero. |
| = | Missing grade - Indicate how you want missing grades to be treated. Select one of the following: |
| = | Ignore Grade Item - removes the grade item from both the numerator and the denominator. |
| = | Count Item as Zero - enters a value of zero in the numerator and leaves the corresponding credit value in the denominator. |
| = | Level - Select one of the following: |
| = | Use Assigned Level - this uses values from the version of the grading table specified for the course (e.g., Honors, Remedial). |
| = | Use Regular Level - this uses values from the Regular version of the grading table, regardless of the course level specified for the course. The name of this option may be different if your district has changed the name of the Regular course level setup list item. |
| = | Historical values - Select one of the following: |
| = | Use unweighted values from historical |
| = | Use weighted values from historical |
| = | Start from grade level - Select the grade level to go back to when calculating cumulative GPAs. Note: This only applies if yearly historical values are being used by the system, rather than overall historical values. |
| = | Historical scale - Enter the scale to be used when using GPA values in historical records. For example, if you enter 4 and the GPA value in the historical records is 3.29, PowerSchool SMS takes 3.29 to be on a 4 point scale. If you enter 5, the calculation is 3.29 on a 5 point scale. Note: This only applies if the Calculation Method is Use numeric values scaled to 100. No scale is required for grade points. |
| 5 | Under Calculation Display Result, select how many decimal places the resulting GPA should be rounded to when displaying the result. Note: This is the display precision, not the calculation precision. When PowerSchool SMS does its calculations, it uses the internal value with more decimal places, and then rounds and displays the result in the number of decimal places you specify here. Therefore, the results might not be the same as calculating using the displayed values. You can, however, use the Cumulative GPA report to print displayed precision values for comparison. |
| 6 | Under Contributing Courses, to include all courses in the GPA calculation, select Include all courses in the calculation. |
| = | To include only certain courses in the GPA calculation, select Include selected courses in the calculation. Click 0 courses selected. On the Select Courses page, search for and select the courses included in the GPA, and click OK. Note: If courses are selected they display in a table. |
| = | To exclude only certain courses from the GPA calculation, select Exclude selected courses from the calculation. Click 0 courses selected. On the Select Courses page, search for and select the courses excluded from the GPA, and then click OK. |
| 7 | Under Historical Pages, select Store in historical pages upon year end processing and print on student transcript report, if required. Note: You can only select this option for one weighted and one unweighted cumulative GPA definition.The GPA definitions with this setting appear on the Grade Point Averages page, preceded by an asterisk (*). |
| 8 | Click OK. |

www.powerschool.com
Tel: 866-434-6276
Email: smssupport@powerschool.com
Copyright 2015-2016 PowerSchool Group LLC and/or its affiliate(s). All rights reserved. All trademarks are either owned or licensed by PowerSchool Group LLC and/or its affiliates.