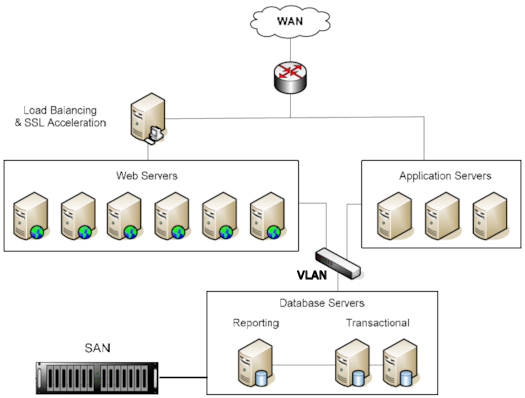
For a system subject to large data or traffic demands, running several instances of each type of server [>>] facilitates the balancing of traffic loads, increases data security, and boosts fault tolerance (and thus overall system availability). A multi-server configuration also facilitates the separate processing of PowerSchool SMS's several distinct tiers of logic such as those for presentation, reporting, transactions, meta data, and the database [Figure 166]. Finally, dedicating each server to only selected roles improves performance [>>].
Determining the appropriate number of servers needed for a system involves taking the following into consideration:
| = | The number of students: Affects the amount of storage space needed. |
| = | The number of teachers: Affects the number of Web Servers needed to support concurrent users. |
| = | PowerSchool SMS modules in use: Affects how application load processes need to be spread across servers. |
| = | The growth of the district: We recommend hardware that will perform well for at least four years. |
| = | Ratio of Web Servers to Application Servers: We recommend a ratio of four to two. For a highly available system, we recommend at least two Application Servers. |
Figure 166: A multi-server configuration

Load Balancing: This application balances traffic loads between the Web Servers. Windows Server 2008 supports Network Load Balancing. However, on larger-scale implementations, we recommend moving this extra computational load to a separate dedicated device.
SSL Acceleration: Performs hardware acceleration for the secure connections (SSL). SSL connections offer better security for student data. Windows Server 2008 supports SSL acceleration. However, on larger-scale implementations, we recommend moving this extra computational load to a dedicated device.
VLAN: A Virtual Local Area Network connects the Web and Application Servers to the Database Servers. PowerSchool SMS employs a multi-level security system based on standard .NET and SQL Server security.
Database Servers: The Reporting Database Server uses Microsoft SQL Server Transactional Replication to maintain its consistency with the Transactional Database Servers.
SAN: The database resides on a Storage Area Network (SAN) or other high availability storage device. This storage device is necessary for a high-availability multi-server environment.
Pearson
Always Learning
www.pearsonschoolsystems.com
Tel: 866-434-6276
Email: psstechsupp@pearson.com